 |
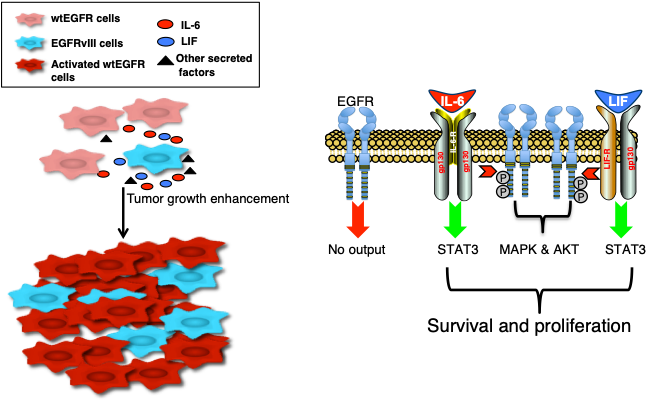
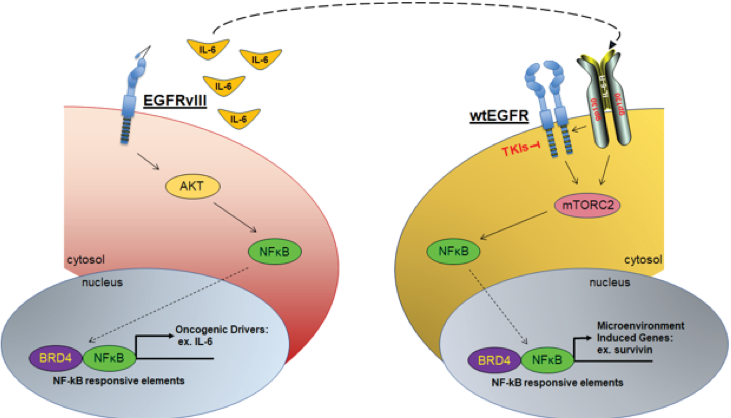
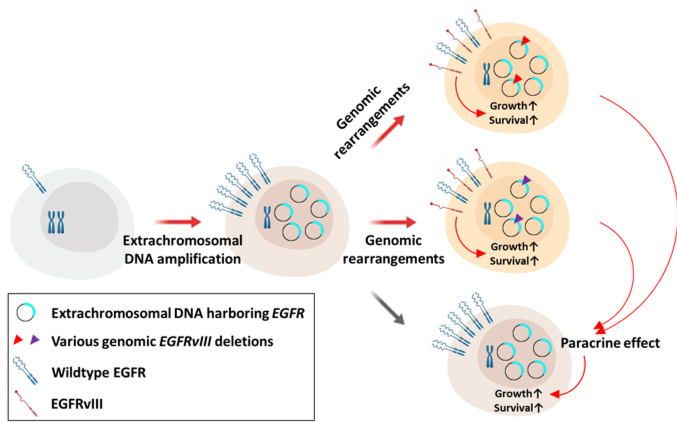
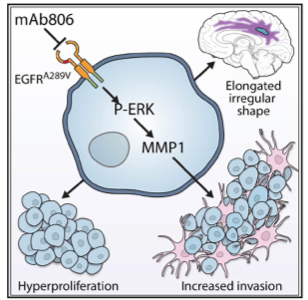
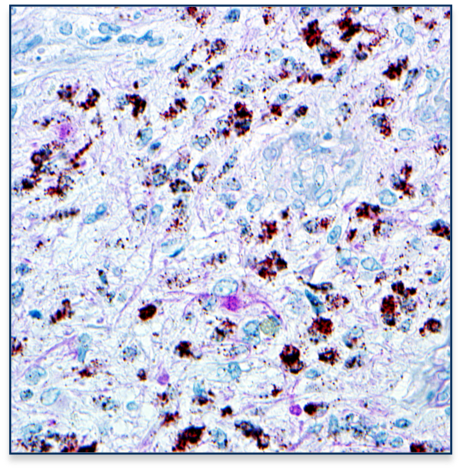
A central issue that confounds successful treatment of GBM patients is the heterogeneous nature of this aggressive tumor. As a result, multiple and spatially distinct heterotypic populations exist within a single GBM, making any lesion- or pathway-specific therapy less effective. While considerable effort has been placed on understanding cell intrinsic mechanisms conferring therapeutic resistance, much less is known about the interactions between heterogeneous tumor cells within these neoplasms that contribute to the recalcitrant nature of this cancer. |